Would you buy an iPhone just because your friend asked you to? Or would you do your research before spending your money? We check online reviews and compare products to make sure the seller can be trusted. So why not do the same before buying a share of a company?
Before we start investing, we need to know if it is safe to invest in a company. We need to understand the company's long-term plan and its financial health. Simply put, we need to check the background of the company. Such background research helps us make better investment decisions. The best source for obtaining such information is the annual report.
What is an Annual Report?
The annual report is a document that contains a summary of the important activities that the company carried out during the year. It also includes financial performance.
This also acts as the company's official announcement to its shareholders(It is a group of people who have an interest in the decisions that the company makes).
They are those who can affect or be affected by the company's operations. For example, for investors, employees, customers, suppliers, etc.
Importance of Annual Report:
Would you trust an outsider to provide information about the company? Or would you trust the company itself?
The annual report is the official document of the company. This report is essential for an informed investment decision. It is an important resource for conducting a fundamental analysis of a company.
Annual reports are lengthy, so we've skimmed through a few important sections that you absolutely must go through. By going through these sections, you can focus on what's important.
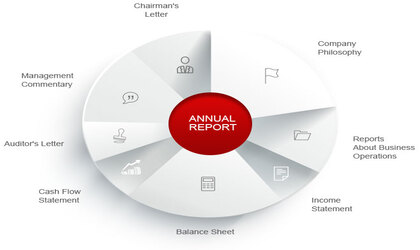
Important elements of an Annual Report:
1. Company Profile
The main reason why we must understand a company’s profile is that it answers all these questions –
- Which industry does the company fall under?
- Who are its clients?
- Which and how many products is the company offering?
- Who are their competitors?
- Check for its global presence- It is important to know the company’s structure to make qualitative interpretations. For example, by knowing their competitors, we can compare two companies to shortlist the best one.
2. Financial Statements
Financial statements are one of the most important items for understanding a company. It provides information on the company's financial performance and position. These statements can be used to check the company's past and potential performance.
Later we will understand how to parse these statements from scratch. For now, let's understand the structure and their breakdown.
There are three basic statements –
a. Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet provides the company’s financial position at a given point in time. There are 3 main components in a Balance Sheet –
- Assets: What the company owns.
- Liabilities: What the company owes to its stakeholders.
- Equity: Shareholders’ stake in the company.
The assets and liabilities reported in the balance sheet play an important role in decoding a company’s financial health.
b. Profit and Loss Statement
A profit and loss statement shows the income and expenses of a business for a certain period.
Revenues refer to income from the primary sources of business. Other income may include profits that may or may not arise in the ordinary course of business.
Expenses consist of monetary and non-monetary expenses paid during the year. For example, administrative costs, rent paid by the company, wages paid, etc.
Net income is the profit that is left over for the company after all expenses have been paid. Net Income = (Sales + Other Income – Expenses)
If expenses exceed revenues and other income, the company records a net loss.
c. Cash Flow Statement
A statement of cash flows records all cash activity of a business. This statement helps us track all cash transactions (inflow and outflow) in isolation. The liquidity, solvency, and financial flexibility of the company can be checked.
There are 3 broad categories of Cash Flow Statements –
- Cash Flow from Operating Activity – Comprises the day-to-day operations of the company.
- Cash Flow from Investing Activity – Comprises investments made by the company. For example, the acquisition or disposal of long-term assets.
- Cash Flow from Financing Activity – Comprises transactions involving debt and equity.
3. Corporate Governance
How will the company grow if there is internal strife? An investor will not want to park their money if internal management is in conflict.
Corporate Governance is the set of rules and laws by which businesses operate. They ensure ethical behavior and practices within the company.
Strong corporate governance serves to give investors a sense of protection. This is reflected in the company's operational efficiency and better financial performance. Poor corporate governance often leads to corporate failure. It hinders the company's ability to identify and manage risks.
A few questions for investors to consider when assessing a company's governance:
1)Who represents the shareholders on the company's board of directors?
2)Who are the significant investors in the company?
3)How strong are shareholder rights?
4)Check their policies and credit score.
How does the company manage long-term risks? (such as human capital management, long-term sustainability, etc.)
4. Chairman’s Message or Director report
The director's report provides a brief overview of the company's past performance. It discusses the future strategy that the company plans to implement. In this section, you will learn about the company's key developments.
It shows whether the company complies with financial regulations and other obligations. We encourage you to read the director's report for the past three to four years to get a bigger picture of the company's progress.
One of the most important factors to check here is the distribution of capital. How much capital is issued as a bonus and how much is retained by the company?
The chairman's report is usually followed by a question-and-answer session with the company's CEO. Various trends, strategies, and developments are answered here.
5. Auditor’s Report
After completing the financial statements, the auditor reviews the accounting records. They check and verify the reliability of the reported numbers. Here you can read the auditor's unbiased opinion on the company's financial statements. There are usually made up of three paragraphs –
- Responsibilities of the auditor
- The purpose of the audit
- Auditor’s findings and opinions.
Conclusion:
Annual reports are one of the most reliable sources for gathering important information. They help us make investment decisions and identify warning signs.
To summarize, the annual report acts as a map of lost waters where you are the captain of your ship. The best way to start is to read your first annual report. If you want to become an investor, make reading the annual report a mandatory ritual before you decide to invest in a company.








 1,499
1,499